
Online marketing is constantly changing, and things won’t slow down in 2021. As you plan for a new year, it’s necessary to know what works and what doesn’t. While some strategies are essentially timeless, some current trends are important to understand and implement right now.
The following is a guide to help you develop a 2021 online marketing strategy to get your business found in more searches.
1. Develop Content That’s Rich and Fresh

Content is still just as important as it’s ever been if you want to rank in search engines. However, it’s all about the quality over the quantity of content and keywords. Google appreciates readable content that people find easy to digest. It won’t matter how many keywords you add or the number of H tags, links, images, and videos you embed within – Google won’t reward old-school Search Engine Optimization (SEO) practices.
Keywords are still important, but they aren’t the basis for your content the way they used to be. First and foremost, write for readers, not Google. If you can write engaging content that people actively read and are willing to share, this could signal to Google that the content is worth ranking over competitors.
People like to reach the information they are looking for quickly, so use lists, bullet points, and graphic elements so the reader can quickly skim through and find what they need. Consider writing about new key topics and include sub-topics in an easy-to-read hierarchy that is simple to follow.
2. People Want to ‘Experience’ Interactive Content

The growing volume of content out there also makes it harder to stand out unless you manage to reel people in with uniquely engaging content. If you want to grab and hold people’s attention with your content, creating interactive content can help.
People are getting used to connecting with all types of content as they immerse themselves in virtual experiences of all kinds. From the use of various apps to the rise of virtual and augmented reality, just about anything can be interactive for consumers, which they are beginning to seek.
Videos may be your fastest way to create more interactive content. People’s attention spans are short, and they would rather watch a quick video than read a long article. Video helps with their multitasking, and they can watch them on their smartphone or tablet. That is why Google’s algorithm has given high priority to videos. After all, search engines are where people primarily engage with videos.
Consider these statistics from the latest WZYOWL survey:
- Video is used by 85% of businesses, with 92% seeing video as a critical aspect of marketing strategies.
- 87% of video marketers noted there is an increase in website traffic due to their videos.
- 96% of people watch explainer videos about services or products.
- 84% of people say videos convince them to purchase a product/service.
Noted in the same WYZOWL survey, about 20 percent of businesses do not use video in their strategy because of the expense. But they are missing out.
The cost of creating a video does not have to be astronomical. You can create an inexpensive but effective video for your target audience.
- Take the top 10 or 20 pages of your existing content and change them into video content. If you have longer content, divide the important information into individual stand-alone videos that use them on multiple channels.
- Make video interviews with your thought leaders, staff, or customers about something valuable for your target audience. You can also conduct customer interviews for case studies, using it as testimonial material on your website.
- Publish webinars on your website or YouTube channel (do both even).
- Turn podcast recordings into a short specific topic video using the audio interview over a motion/illustrated graphics video.
Ensure that you optimize your video content for YouTube, including the titles, thumbnails, metadata, etc. If hosting on your site, ensure your videos are optimized for lazy loading to reduce the risk of ranking problems due to slow page speeds.
Use each social media’s live video feature. YouTube, Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and other social media sites offer a live video feature. Create a live video with company leaders or stakeholders talking about the organization, products, or services. Since the social media platforms have built this capability into their sites, there is not much production you need to do. Also, keep the discussion light and informal to reach out to your audience. You want to come across as authoritative but approachable too.
3. Set Specific Goals for Your Content

Companies often have a single goal in mind when they create new content: Get tons of traffic. Getting plenty of traffic is usually a worthwhile goal, but you may need to get more specific with your goals in many cases.
For example, you could have a page that generates hundreds of views over a month, but it doesn’t mean anything if those people leave the page and don’t become leads. What you want to do is make sure your content attracts the right people at the right time. Again, it comes down to quality vs. quantity.
Consider what types of content people are looking for at different stages of the buyer’s journey, from prospects to repeat customers. You could have blog posts that serve to educate and inform people doing basic research around a topic. From there, they may want to learn about solutions to the specific problems they have, which you may be able to provide in more middle-of-funnel blog posts. Once people are at the decision stage, your content could discuss why your products or services are right for them. To push sales, you might lead people to service or product pages to make a purchase or to a contact form to request a quote or consultation.
Ultimately, it would be best to think about the specific intent behind each piece of content you create and what readers are looking for when they encounter it.
4. Take EAT into Consideration

The concept of Expertise, Authority, and Trust (EAT) has become one of the key concepts relating to SEO. Essentially, EAT is all about trying to establish yourself as an authority in your industry and a reputable thought leader that people can trust. If you can prove to both Google and prospects that you have the expertise and authority needed to be trustworthy, this could be beneficial to SEO.
While high-quality content matters to Google, so does the intent and credibility of the content creator. If Google finds that you aren’t able to prove that you have the knowledge or credentials to support your website and the information you provide, this could hurt your rankings in the long term. Whether you receive bad customer reviews on Google or Yelp, or people stop visiting your website because they don’t perceive it as trustworthy, Google will take notice and punish your website accordingly.
5. Optimizing for “Position Zero”
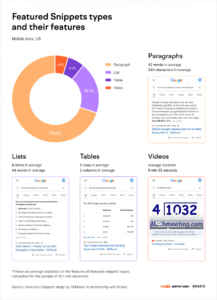
While many businesses tend to aim primarily for the first spot in Google Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs), the most coveted position today is what’s known as “position zero.” Specifically, you want to rank for the Google Featured Snippet, which will make sure you have the chance to be seen even before the top-ranking paid ads in SERPs.
The featured snippet gives people a brief piece of information based on what they enter in Google Search. The snippet made its first appearance back in 2014, but it has since become an essential spot to obtain in rankings with subsequent algorithm updates.
The beauty of snippets for users is that the person performing the search never needs to leave the search results page. They can get the information they want without clicking over to another website, but this advantage can be a disadvantage to businesses trying to draw traffic. However, you can encourage people to visit your website if you rank for this snippet while offering just enough information to hook them to the primary source. People are also much more likely to trust the information that appears in snippets because it looks as if Google ‘handpicked’ the text.
6. Incorporate Semantic Search Tenets
As SERPs have become more advanced, they no longer depend on precise phrasing to deliver results. Now, they can analyze the objective of a search and pick up on the contextual implication of search phrases when connecting users with the content on websites. Semantic search is comprised of two central tenets:
The Intention of a Search.
Google is now considering the motivation behind any search inquiry. Users have specific goals in mind, and that’s why they use search engines. Some users may be conducting research, looking to educate themselves. Others may be looking for a specific product or service and some ‘type in’ their search terms to purchase. When search engines consider a user’s intention, they can better ‘handpick’ the results the user is seeking out. For users conducting research, for example, search results provide answers from reputable sources. For users seeking out a specific service, search results list top brands.
The Semantic Significance of Terms Used in a Search.
Semantics looks at the link between individual words and studies how they are related when they’re used together. When referring to SEO, semantics correlates to the significance of search terms, what other search terms are closely associated, and finally, the grouping of words on a website. When semantic significance is considered, SERPs can employ intelligent matching, linking users to results that better provide the answers they’re looking for.
Consider the evolution of search phrases. Previously, keywords were the hot topic when it came to SEO. However, this method became vulnerable to misuse. People began to stuff keywords into their content, creating a poor user experience. With this limited system, users had trouble finding what they were looking for. Now, with semantic search, users can input a query and be flooded with relevant content that enhances their experience, seemingly reading their minds and offering additional ideas to complement their original inquiry.
7. Pay Attention to the Four Main Categories of Search Intent

To expand on the first semantic search tenet above, Google’s BERT algorithm looks beyond target keywords, using machine learning and natural language processing to decipher search phrases better. While your website may have great content, if it’s not matching up with a user’s search intent, you’re not going to rank high on search results pages. For instance, coffee may be the primary keyword used across your content. But users could have different intentions when inputting ‘coffee’ into a search engine. They may be looking for a local coffee shop, they may be looking for ground coffee to purchase online, or they may be looking for a coffee maker to add to their kitchen collection.
Begin incorporating user intent into your overall content marketing strategy. Users are looking for satisfaction online; when your content provides the value they need and is relevant to what they’re searching for, you improve your website’s ranking.
Backlinko breaks down search intent into four main categories:
Informational
An informational search intent comes from a user who is seeking out more information on a particular topic. Sometimes, that means they’re looking to define words or concepts, sometimes they may be seeking out a complete guide to performing a specific function, and other times they may be looking for a recipe to create a particular dish. Informational search intent is not always posed as a question either. Sometimes, a user may input the name of a public figure, for instance, to learn more about that person. Information search intent phrasing may look something like this:
-
- How to write a blog post
- Where is Area 51
- Elon Musk
- Directions to ORD airport
Navigational
Users with navigational search intent are looking to be directed to a specific web page, and they use a search engine because it facilitates the process. It could be the URL is too long to type out, or they’ve forgotten the complete name of the website they’re searching for. On other occasions, the website may have many pages, and instead of clicking throughout the website to find what they’re looking for, they ask Google to bring up that specific page for them. Navigational search intent phrasing often includes the name of a website or a brand name. Some examples are:
-
- Microsoft LinkedIn
- WordPress login
- Amazon customer service
- SearchLab SEO tips
Commercial
When a user has a commercial search intent, he has moved past the informational stage and is now comparing products and services before deciding to purchase. At this stage, a user is conducting commercial research to narrow down options and focus on comparing features, benefits, and pricing. Some examples of commercial search intent include:
-
- Chromebook vs. Macbook
- Best Italian restaurant near me
- Shopify or WooCommerce for e-commerce
- Best dog carrier for air travel
Transactional
Users with transactional search intent have made a decision, and they’re ready to buy. They know what they want, and they’re prepared to complete a transaction. Since they’re familiar with what they’re looking for, they’ll typically use branded search terms. Examples include:
-
- TikTok leggings
- Shop Michael Kors purse
- JUUL device sale
- RetailMeNot coupon
8. Add ‘Google My Business’ to Your Overall SEO Strategy
With Google My Business, you are provided with a virtual storefront that lets you engage with your customers – all at no cost. Google My Business is an essential part of your overall marketing strategy because it controls a user’s first impression of your business. With Google My Business, you can provide a quick snapshot of your company, including hours of operation, customer reviews, phone numbers, photos, and even product inventory (car dealerships love this). According to Yoast, there are three main factors to consider when setting up your Google listing:
Relevance
Your listing should include details about what your services or products are all about. Ambiguity is not your friend here. Specificity helps you line up with user intent. Consider what users are looking for and position yourself to be at the top of their results.
Proximity
Local businesses heavily rely on proximity for showing up on a user’s search results. You won’t show up on search results for a user in another state. You need to be including your location and including other location-specific content on your website. Though the method Google uses to display local businesses to users is unknown, it does take into account a user’s location when providing a list of related search results.
Prominence
Prominence refers to the amount of activity on your business listing. Is it buzzing with reviews and updated with new photos that display recent events, product sales, or service coupons? Think of it this way – everybody loves a hot spot. Imagine walking downtown in a big city – most people gravitate to the bar with lively music that’s roaring with laughter. Your Google listing should be buzzing with activity, including prompt replies to all your customer reviews. Keep it fresh and updated, just like the content on your website.
9. Manage Your Online Reputation

This piece of your marketing strategy should never be overlooked. Reputation management is how you respond to all mentions of your business online. This includes positive reviews, negative reviews, and other highlights, such as blog posts and news articles. If you’re anything like most users online, you turn to reviews before deciding to move forward with a product or service.
Reviews demonstrate the benefits of your business through the words of previous customers. This inspires trust in new customers and helps them get an inside look at your overall customer experience. If you’re not already connecting your reviews from Google, Yelp, or any other location to your website, you’re missing out. When you implement a review widget that pulls reviews right into your homepage, you’re more likely to convert visitors who may be on the fence about moving forward with a purchase. A few encouraging words from a previous customer may be all someone needs to decide to buy.
You should be moving quickly to respond to reviews as well. A negative review can quickly turn off a potential customer, but how you respond to a negative review can keep them interested in your brand. Overall, reviews offer free advertising, improve your SEO ranking, and demonstrate how well you engage with your customer base.
That’s Your 2021 Online Marketing Strategy to Get Your Business Found in More Searches
When you look at your online marketing strategy as a whole in 2021, you can improve your rankings and enhance brand recognition. From developing optimized and goal-oriented content to aiming for position zero and considering semantic search tenets, you can create an online marketing strategy that covers all bases and places your business in a position to be found in more searches. Take a look at your current content and identify where you can edit to align with search intent. Be sure your Google My Business listing is a hot spot by keeping it updated, and don’t forget to reply – always promptly – to all your reviews.
